Global Technology News.
-
3 Posts
-
3 Photos
-
0 Videos
-
Web Marketing Executive at Market Research Future
-
Lives in New York
-
From New York
-
Studied MCA at USA UniversityClass of A
-
Female
-
Single
-
31/12/1998
-
Followed by 0 people
Recent Updates
-
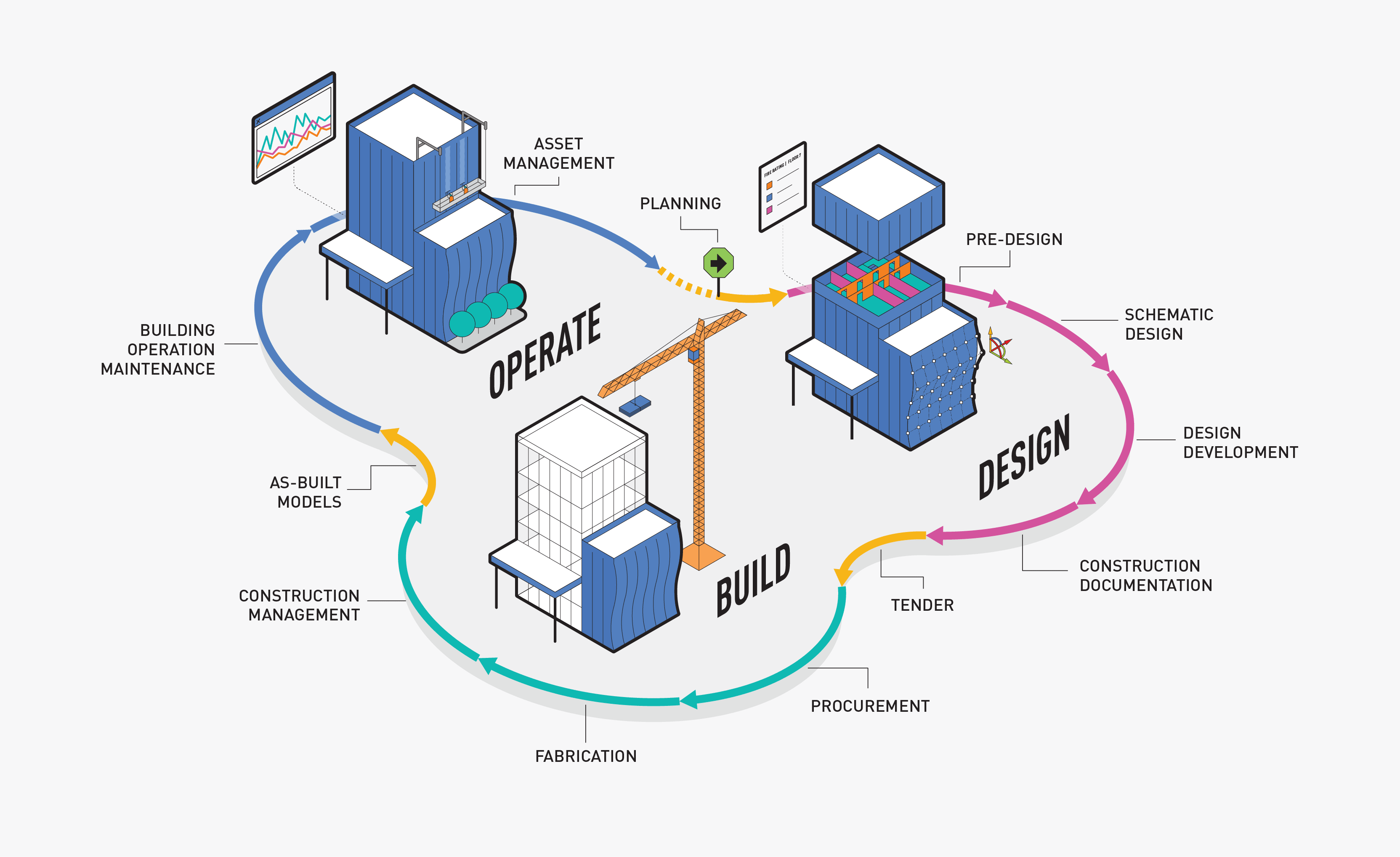
Building Information Modelling (BIM): Revolutionizing the Future of Construction and Infrastructure
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is redefining how we design, build, and manage infrastructure in the 21st century. At its core, BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. This intelligent 3D model-based process provides architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals with the insights and tools needed to plan, design, construct, and manage buildings more efficiently and effectively.
Source - https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/building-information-modelling-market-2044
Over the years, BIM has grown from a simple visualization tool into a collaborative methodology that supports every phase of a building’s lifecycle. From the initial concept and detailed design to construction, operation, and eventual decommissioning, BIM integrates data across all stakeholders. This comprehensive approach allows for informed decision-making at each step, reducing risks and improving outcomes. Whether for a residential apartment complex, a commercial skyscraper, or a massive infrastructure project, BIM has become essential for modern construction.
One of the most valuable aspects of BIM is its ability to foster collaboration among diverse teams. Architects, structural engineers, electrical and plumbing specialists, and contractors can work from the same shared model, ensuring alignment and minimizing errors. By identifying clashes and resolving them digitally before physical construction begins, BIM significantly reduces costly changes and delays. This coordinated approach enhances productivity and drives project success.
BIM also enhances visualization during the design phase, allowing stakeholders to understand exactly how a building will look and function once completed. Through 3D walkthroughs and simulations, potential issues can be spotted early. Design improvements can be made in real time, ensuring the final output is both functional and aesthetically appealing. This leads to better client satisfaction and more streamlined execution.
In terms of cost management, BIM plays a pivotal role. Accurate quantity take-offs and material estimates are automatically generated from the model, offering a precise picture of resources needed. This not only reduces wastage but also facilitates better budget control and financial planning. With this level of detail, project managers are empowered to make data-driven decisions that align with financial goals and timelines.
Sustainability is another key benefit of BIM. By simulating energy performance, lighting, and ventilation, designers can evaluate a building’s environmental impact before construction. This enables the selection of energy-efficient systems, environmentally-friendly materials, and sustainable design practices. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly promoting BIM as a means to achieve green building standards and reduce carbon footprints.
The integration of BIM with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR) is expanding its potential even further. These advancements are transforming how facilities are operated and maintained post-construction. IoT sensors embedded within the building can feed real-time data into the BIM model, allowing facility managers to monitor system performance, detect faults, and perform predictive maintenance. This proactive management not only extends the life of building assets but also enhances occupant comfort and safety.
BIM’s adoption is also influencing regulatory and policy frameworks across the globe. Many countries now mandate the use of BIM for public infrastructure projects, recognizing its potential to reduce costs, improve transparency, and streamline procurement processes. As a result, the global construction industry is witnessing a significant transformation in how projects are planned and executed. The push toward digitalization and smart construction practices is making BIM a standard rather than an option.
Despite its benefits, the implementation of BIM comes with its own set of challenges. These include the initial cost of software and training, as well as the need for a cultural shift toward collaborative working environments. However, as the industry matures and standards evolve, these barriers are gradually diminishing. With proper training and change management strategies, organizations can seamlessly integrate BIM into their workflows and unlock its full potential.Building Information Modelling (BIM): Revolutionizing the Future of Construction and Infrastructure Building Information Modelling (BIM) is redefining how we design, build, and manage infrastructure in the 21st century. At its core, BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. This intelligent 3D model-based process provides architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals with the insights and tools needed to plan, design, construct, and manage buildings more efficiently and effectively. Source - https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/building-information-modelling-market-2044 Over the years, BIM has grown from a simple visualization tool into a collaborative methodology that supports every phase of a building’s lifecycle. From the initial concept and detailed design to construction, operation, and eventual decommissioning, BIM integrates data across all stakeholders. This comprehensive approach allows for informed decision-making at each step, reducing risks and improving outcomes. Whether for a residential apartment complex, a commercial skyscraper, or a massive infrastructure project, BIM has become essential for modern construction. One of the most valuable aspects of BIM is its ability to foster collaboration among diverse teams. Architects, structural engineers, electrical and plumbing specialists, and contractors can work from the same shared model, ensuring alignment and minimizing errors. By identifying clashes and resolving them digitally before physical construction begins, BIM significantly reduces costly changes and delays. This coordinated approach enhances productivity and drives project success. BIM also enhances visualization during the design phase, allowing stakeholders to understand exactly how a building will look and function once completed. Through 3D walkthroughs and simulations, potential issues can be spotted early. Design improvements can be made in real time, ensuring the final output is both functional and aesthetically appealing. This leads to better client satisfaction and more streamlined execution. In terms of cost management, BIM plays a pivotal role. Accurate quantity take-offs and material estimates are automatically generated from the model, offering a precise picture of resources needed. This not only reduces wastage but also facilitates better budget control and financial planning. With this level of detail, project managers are empowered to make data-driven decisions that align with financial goals and timelines. Sustainability is another key benefit of BIM. By simulating energy performance, lighting, and ventilation, designers can evaluate a building’s environmental impact before construction. This enables the selection of energy-efficient systems, environmentally-friendly materials, and sustainable design practices. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly promoting BIM as a means to achieve green building standards and reduce carbon footprints. The integration of BIM with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR) is expanding its potential even further. These advancements are transforming how facilities are operated and maintained post-construction. IoT sensors embedded within the building can feed real-time data into the BIM model, allowing facility managers to monitor system performance, detect faults, and perform predictive maintenance. This proactive management not only extends the life of building assets but also enhances occupant comfort and safety. BIM’s adoption is also influencing regulatory and policy frameworks across the globe. Many countries now mandate the use of BIM for public infrastructure projects, recognizing its potential to reduce costs, improve transparency, and streamline procurement processes. As a result, the global construction industry is witnessing a significant transformation in how projects are planned and executed. The push toward digitalization and smart construction practices is making BIM a standard rather than an option. Despite its benefits, the implementation of BIM comes with its own set of challenges. These include the initial cost of software and training, as well as the need for a cultural shift toward collaborative working environments. However, as the industry matures and standards evolve, these barriers are gradually diminishing. With proper training and change management strategies, organizations can seamlessly integrate BIM into their workflows and unlock its full potential.0 Comments 0 Shares 9 Views 0 ReviewsPlease log in to like, share and comment! -
-
More Stories